Dynlatt: Production- and load-oriented design of cyclically loaded additively manufactured lattice structures made of flexible materials in laser-sintering
Motivation
To make additive manufacturing more sustainable, the DynLatt project aims to establish a workflow of recyclable thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) lattice structures from powder bed-based additive manufacturing. TPU is ideal for applications such as in automotive, transportation industries or medical devices that require repeated bending or compression. 3D printing gives TPU new, interesting possibilities beyond traditional manufacturing processes.
Objectives and Methodology
The main objective is the sustainable use of materials in additive manufacturing, in this project by recyclable TPU instead of resin materials for the series production of components with lattice structures. A modelling approach optimizes the service life and functionality of these structures, reduces material quantities and waste and improves the recyclability of TPU and the sustainability of the manufacturing process.
Innovations and Perspectives
This project will further improve the properties of TPU and open new fields of application. The adaptability of TPU in 3D printing strengthens the value chain through rapid prototype development and customized solutions. This enables flexible production environments, increases the innovation and competitiveness of companies and supports sustainable goals such as resource efficiency and recyclability.
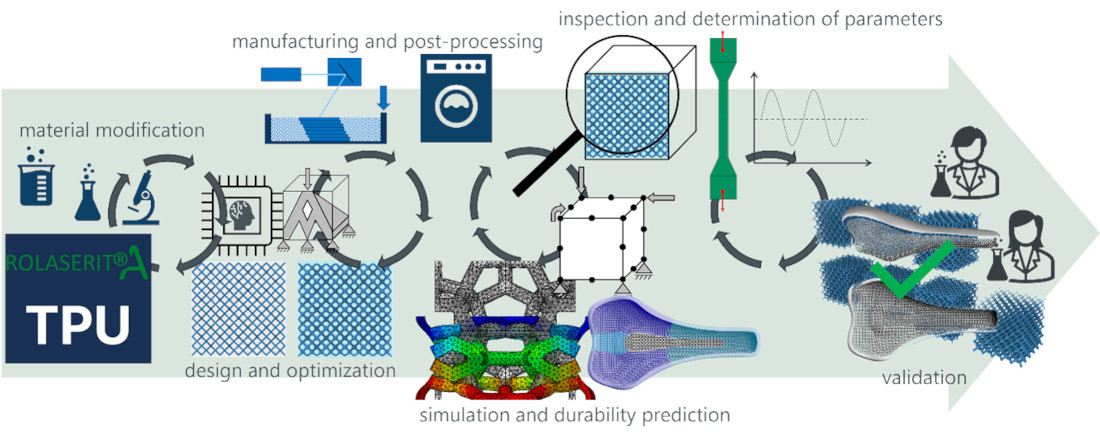
The workflow within the project starts at adapting the material formulation for the needed stiffness and robust processability. Based on those the optimization limits are defined, and optimization strategies are evaluated in combination with experimental testing. In parallel a ML-supported FE-workflow for durability prediction is established and used together with the experimental data for optimizing the projects demo-case.
Contact: Jakub Strugala
Sponsored by the